The Complete Guide to Shoulder Screws: Types, Sizing, and Expert Installation Tips
When it comes to precision fastening, shoulder screws are a game-changer. Unlike standard screws, their unique cylindrical "shoulder" provides structural support and alignment, making them ideal for machinery, automotive parts, and heavy-duty DIY projects. At HomeDIYer, we specialize in high-quality shoulder screws designed for durability and performance. In this guide, we’ll break down the different types of shoulder screws, how to choose the right size, and best practices for installation.
1. What Are Shoulder Screws?
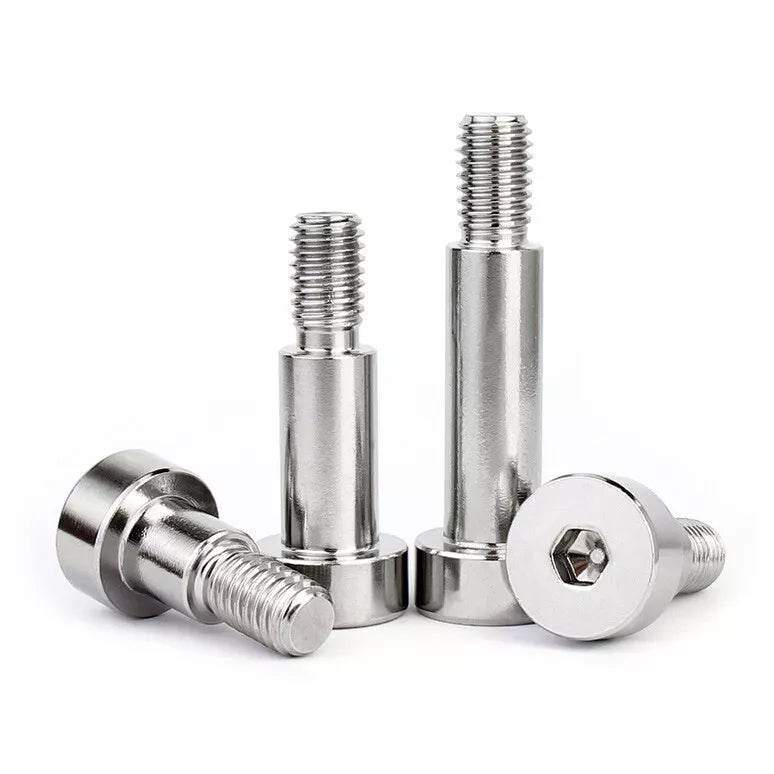
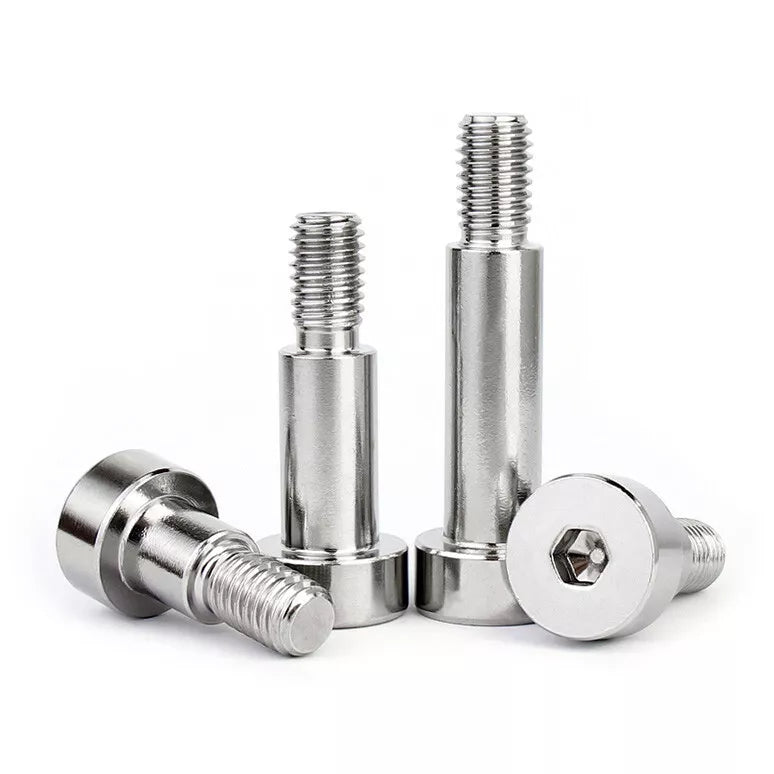
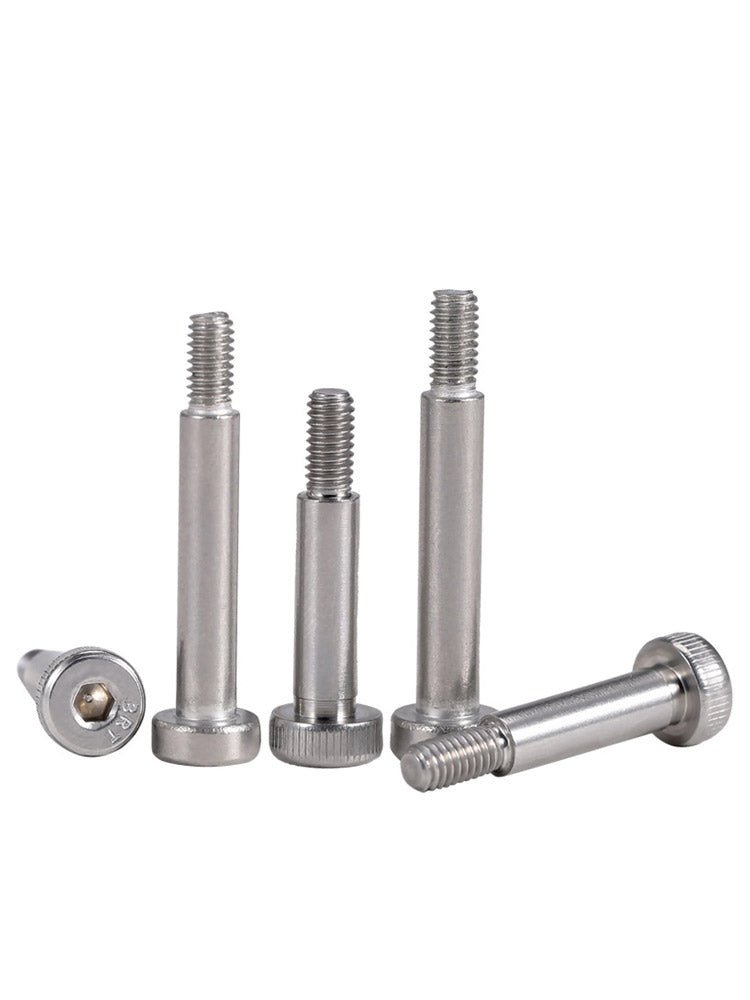
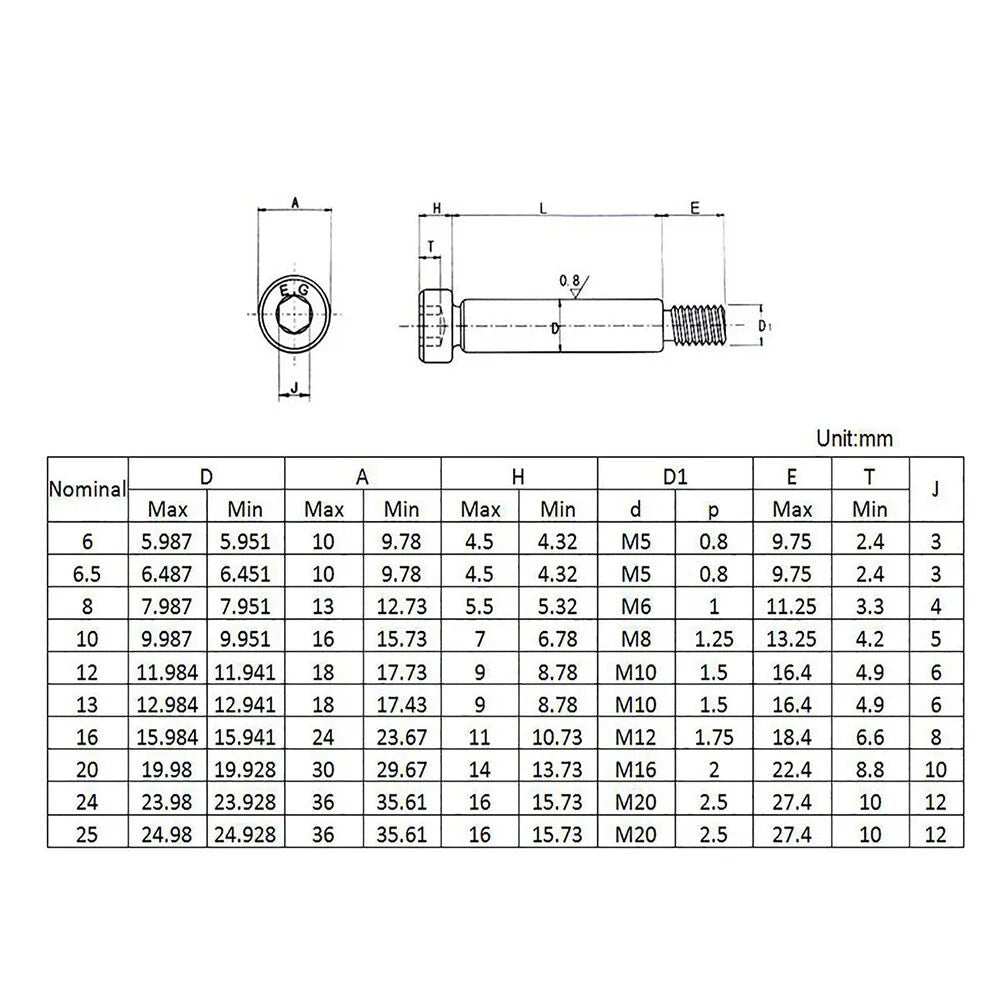
Shoulder screws, also known as shoulder bolts or stripper bolts, feature a smooth, unthreaded cylindrical section between the head and threads. This design allows them to act as pivots, spacers, or alignment guides in assemblies. Common applications include:
- Machinery: Securing gears, pulleys, and rotating parts.
- Woodworking: Reinforcing joints in decks or cabinets.
- Electronics: Mounting components with precise spacing.
Popular variations like socket head shoulder screws (for high torque) and headless shoulder screws (for low-clearance spaces) cater to specialized needs.
2. Types of Shoulder Screws
a. Socket Head Shoulder Screws
These screws feature a hexagonal socket drive, ideal for high-torque applications. Use them in automotive engines or industrial equipment where precision tightening is critical.
b. Metric Shoulder Screws
Designed to international standards (e.g., M3 shoulder screw, 6mm shoulder screw), these are perfect for imported machinery or DIY projects requiring metric measurements.
c. Headless Shoulder Screws
With no protruding head, these screws sit flush in assemblies—great for compact devices like 3D printers or robotics.
d. Stainless Steel Shoulder Screws
Corrosion-resistant options like 18-8 stainless steel shoulder screws excel in outdoor or humid environments.
3. How to Choose the Right Shoulder Screw
a. Sizing Matters
Always check shoulder screw dimensions:
- Diameter: Match the shoulder diameter to the hole size (e.g., 1/4 shoulder screw for 0.25" holes).
- Length: Ensure the threaded section penetrates at least 1.5x the material thickness. For decking, a 3-inch shoulder screw provides optimal grip.
b. Material Selection
- Alloy steel shoulder screws handle heavy loads.
- Brass shoulder screws are non-sparking, ideal for electrical work.
4. Installation Best Practices
a. Spacing and Depth
- Drywall: Space drywall screws 16–24 inches apart along studs. Use 1 ¼-inch screws to avoid puncturing pipes.
- Decking: Position deck screws 6–8 inches apart for stability. A 2.5-inch screw ensures penetration into joists.
- Metal Roofing: Install metal roofing screws 12–18 inches apart along seams.
b. Pre-Drilling Tips
For hardwoods or dense materials, pre-drill pilot holes slightly smaller than the screw diameter (e.g., 3mm pilot hole for a 4mm screw). This prevents splitting and ensures smooth threading.
c. Torque Control
Over-tightening can strip threads. For SSD NVMe screws, tighten just enough to secure the drive without warping the PCB.
5. Common Questions Answered
Q: How tight should shoulder screws be?
A: Tighten until snug, then add a quarter-turn. Use a torque wrench for critical applications like shoulder vise screws.
Q: Should I use anchors for screws in wood?
A: Yes! Screw anchors distribute weight in softwoods or plasterboard. For heavy shelves, opt for toggle anchors.
Q: What’s the difference between shoulder screws and standard screws?
A: The unthreaded shoulder provides rotational stability, reducing wear in moving parts.
6. Why Choose HomeDIYer Shoulder Screws?
Our precision shoulder screws are CNC-machined for exact tolerances, and we offer:
- Metric and SAE sizing (e.g., 10-32 shoulder screw, M5 shoulder screw).
- Durable materials including stainless steel and brass.
- Bulk pricing for contractors and hobbyists.
7. Final Tips for DIYers
- Label screws by type (hex head, flat head) to avoid mix-ups.
- Store shoulder wood screws separately to prevent corrosion.
By mastering the nuances of shoulder screws, you’ll tackle projects with confidence—whether you’re building a deck, repairing machinery, or upgrading your workshop. Explore our Shoulder Screws Collection to find the perfect fasteners for your next DIY adventure!