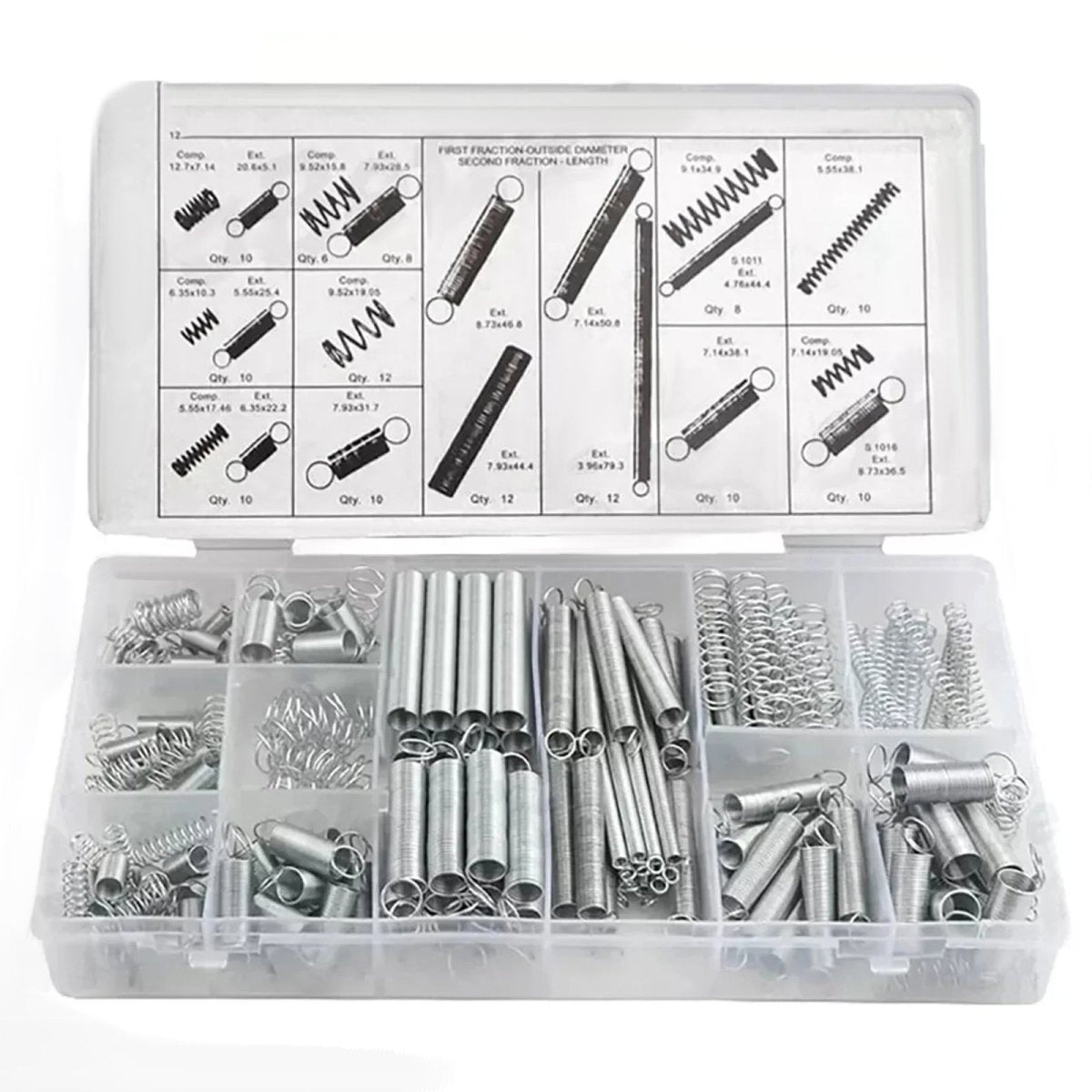
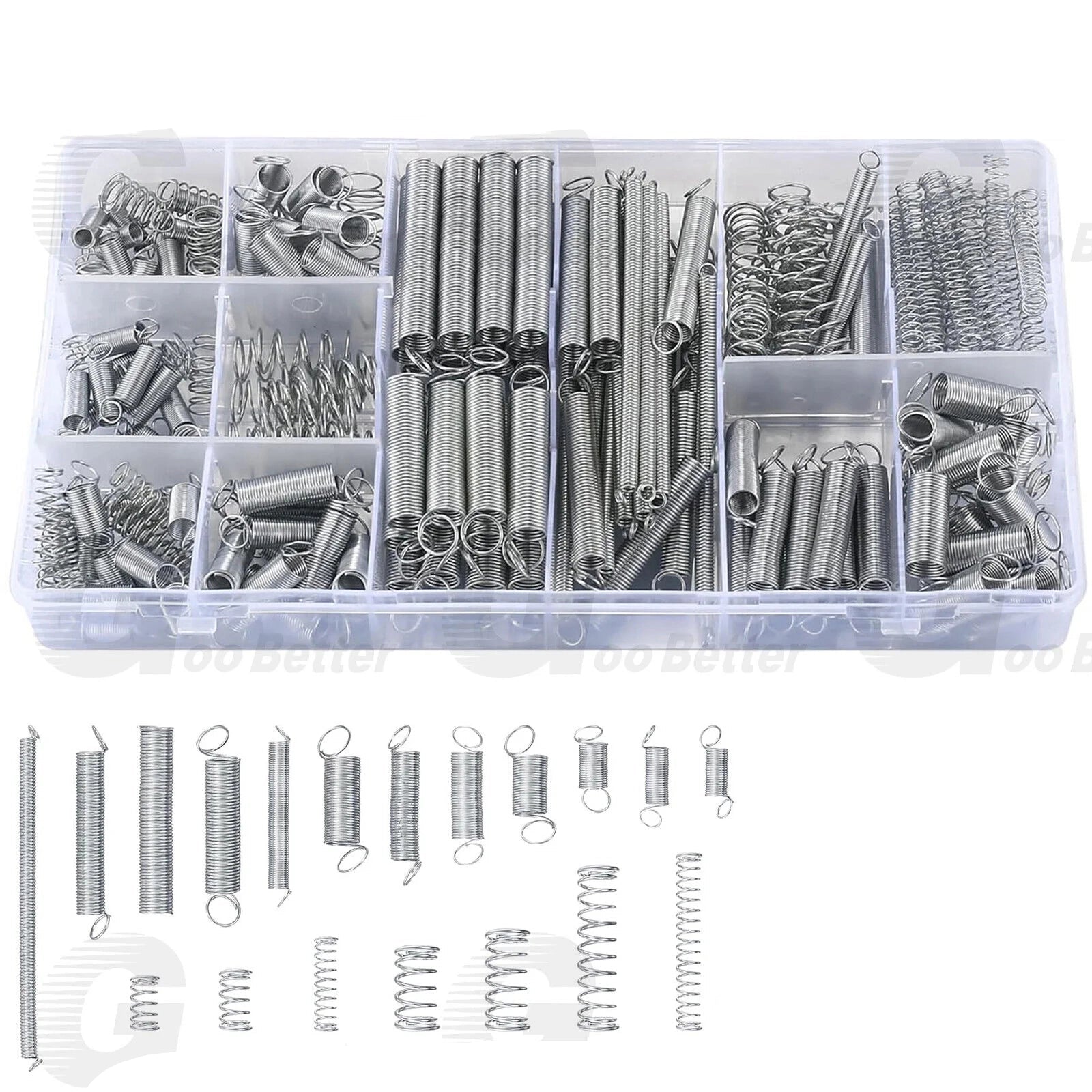
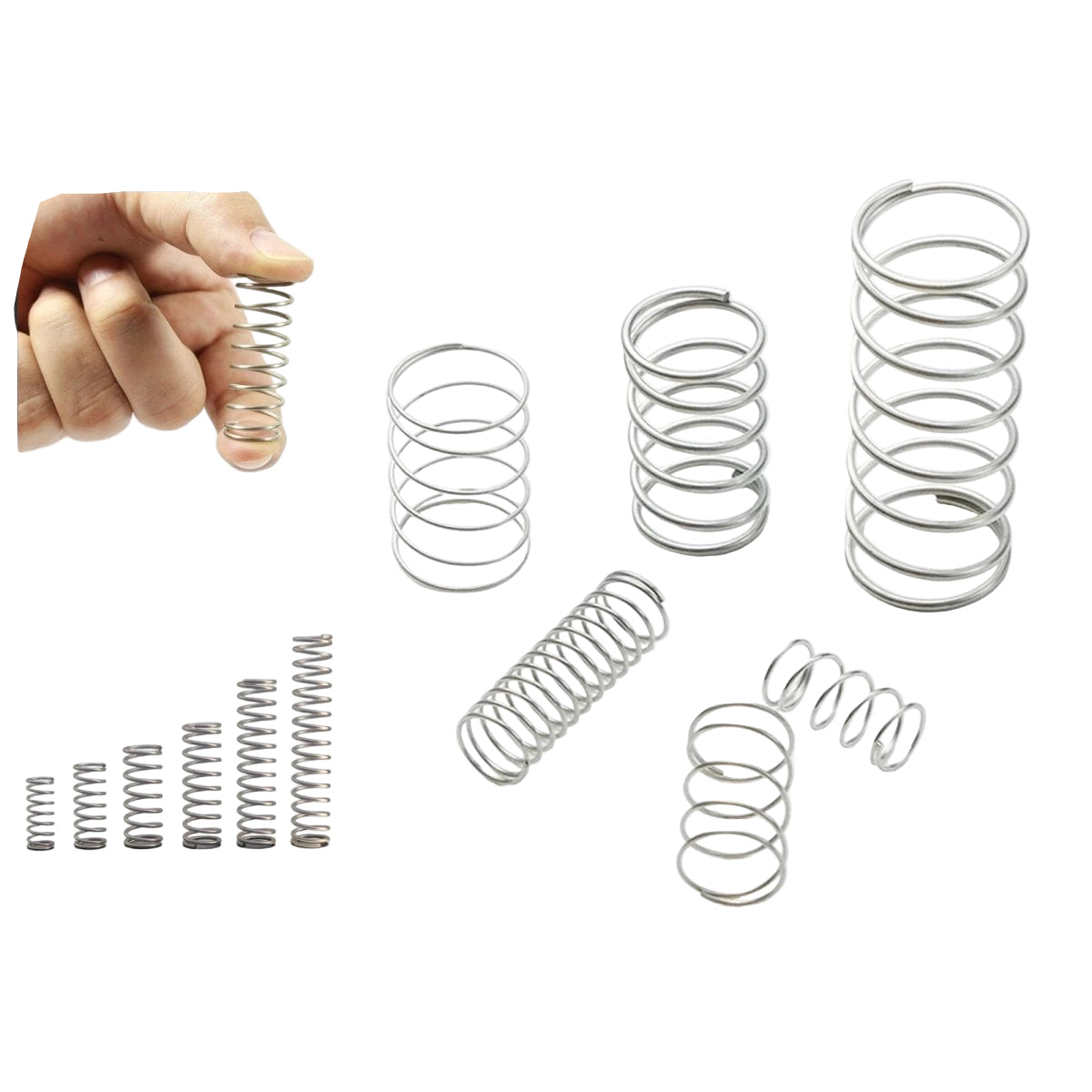
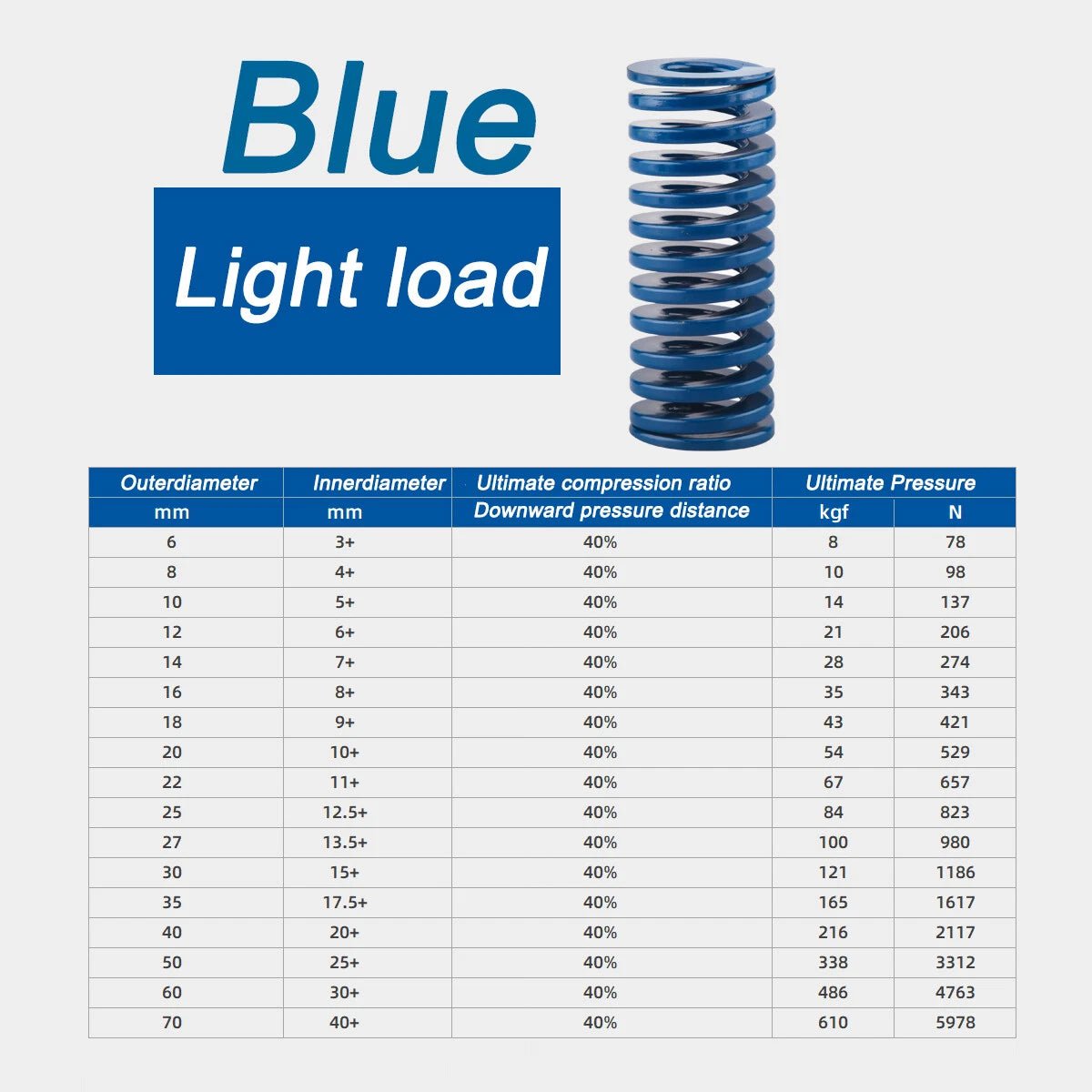
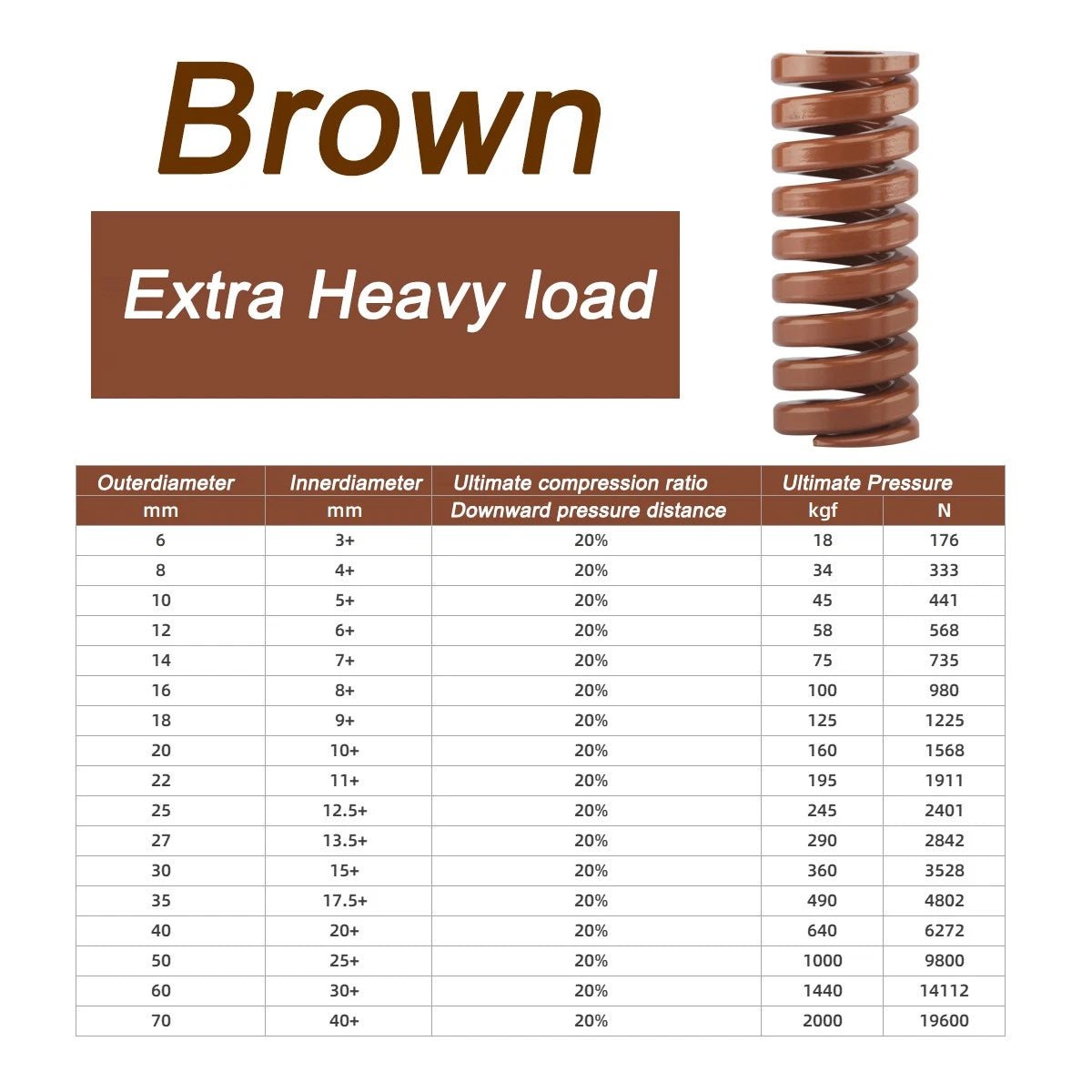
1. What Are Compression Springs?
Compression springs are helical coils designed to resist axial pressure, storing energy when compressed and releasing it when the load is removed. These springs are widely used in automotive suspensions, industrial machinery, and even household appliances. Key types include:
- Standard Compression Springs: Ideal for general applications (e.g., “compression springs by size”).
- Heavy-Duty Springs: Built for high-stress environments (search term: “heavy duty compression springs”).
- Stainless Steel Springs: Corrosion-resistant for outdoor or humid conditions (“stainless steel compression springs”).
Why Choose HomeDIYer? Our springs undergo rigorous testing (see “compression spring testing machine”) to ensure longevity and performance.
2. How to Choose the Right Compression Spring
Selecting the perfect spring depends on three factors:
- Material: Stainless steel offers rust resistance, while carbon steel suits heavy loads.
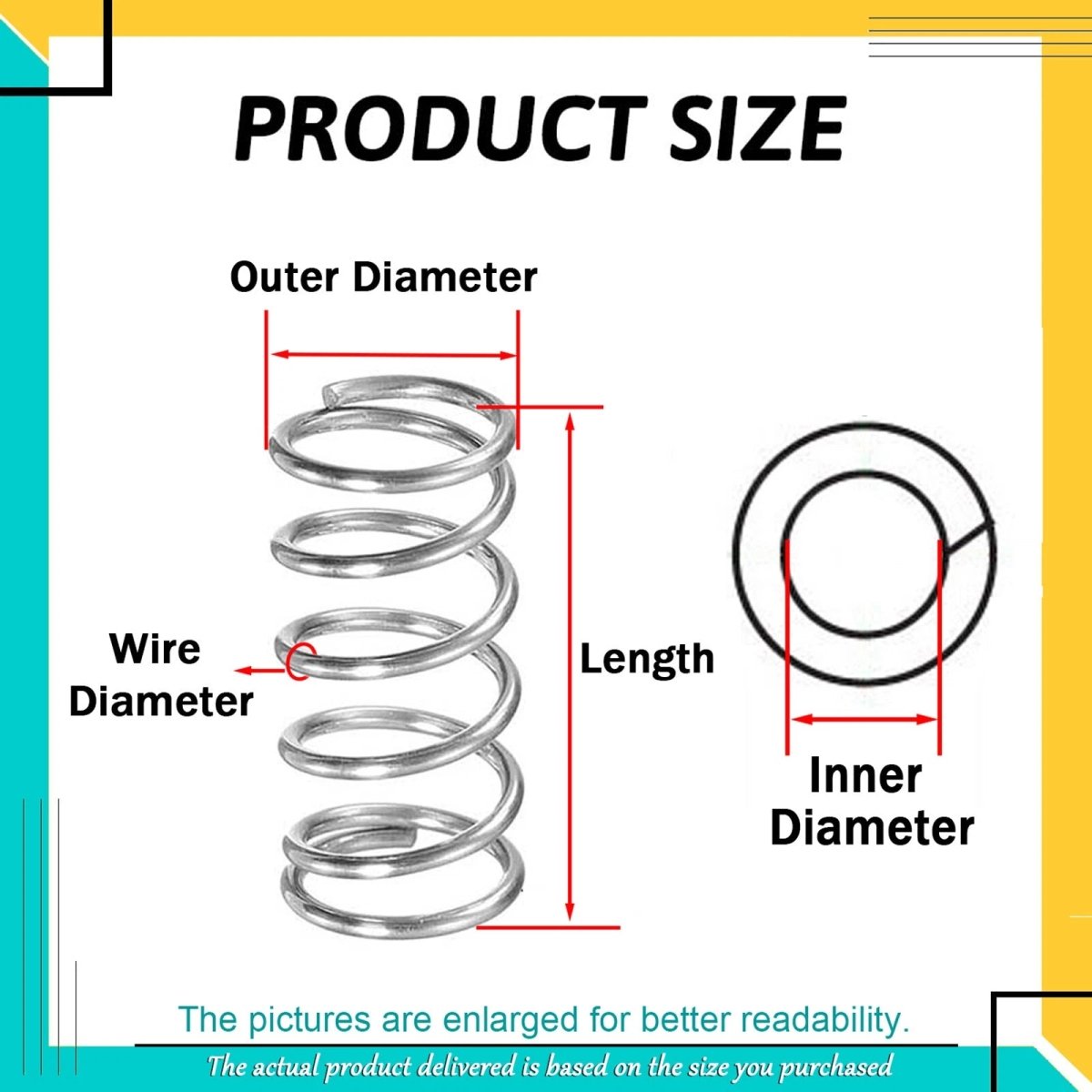
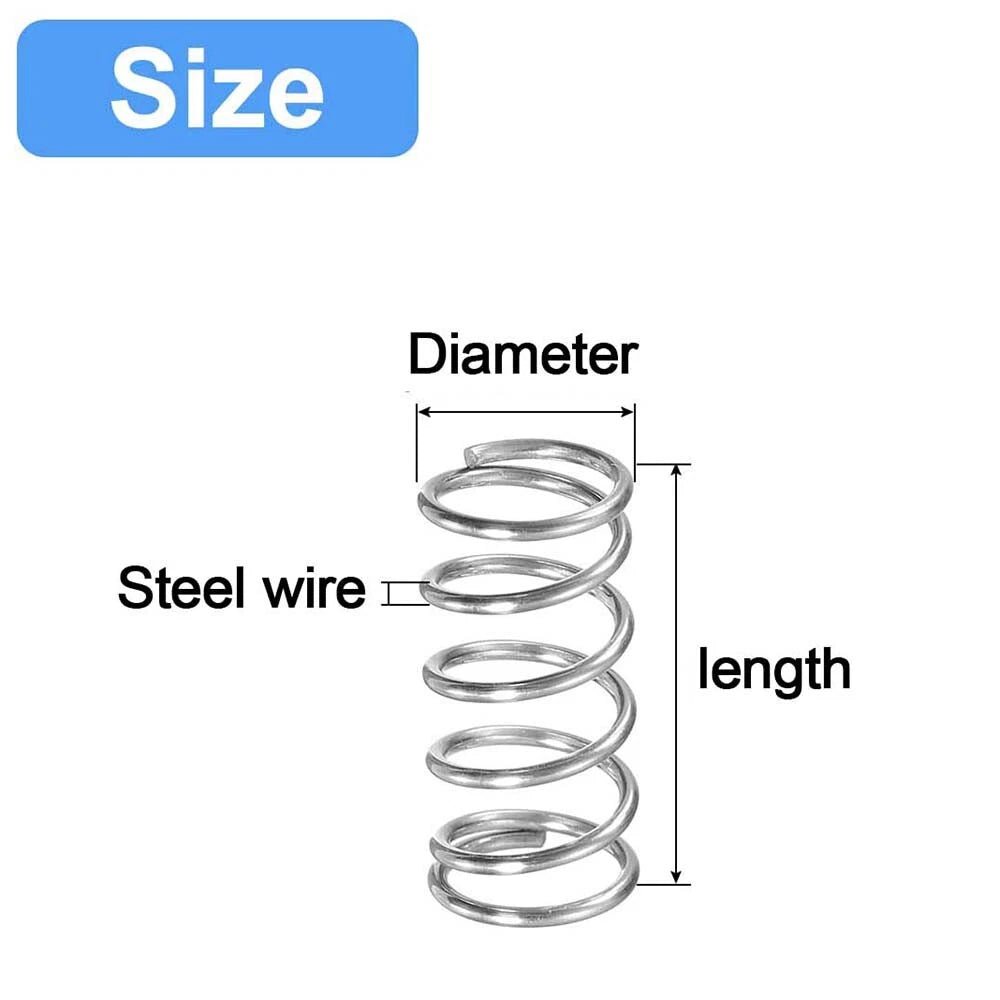
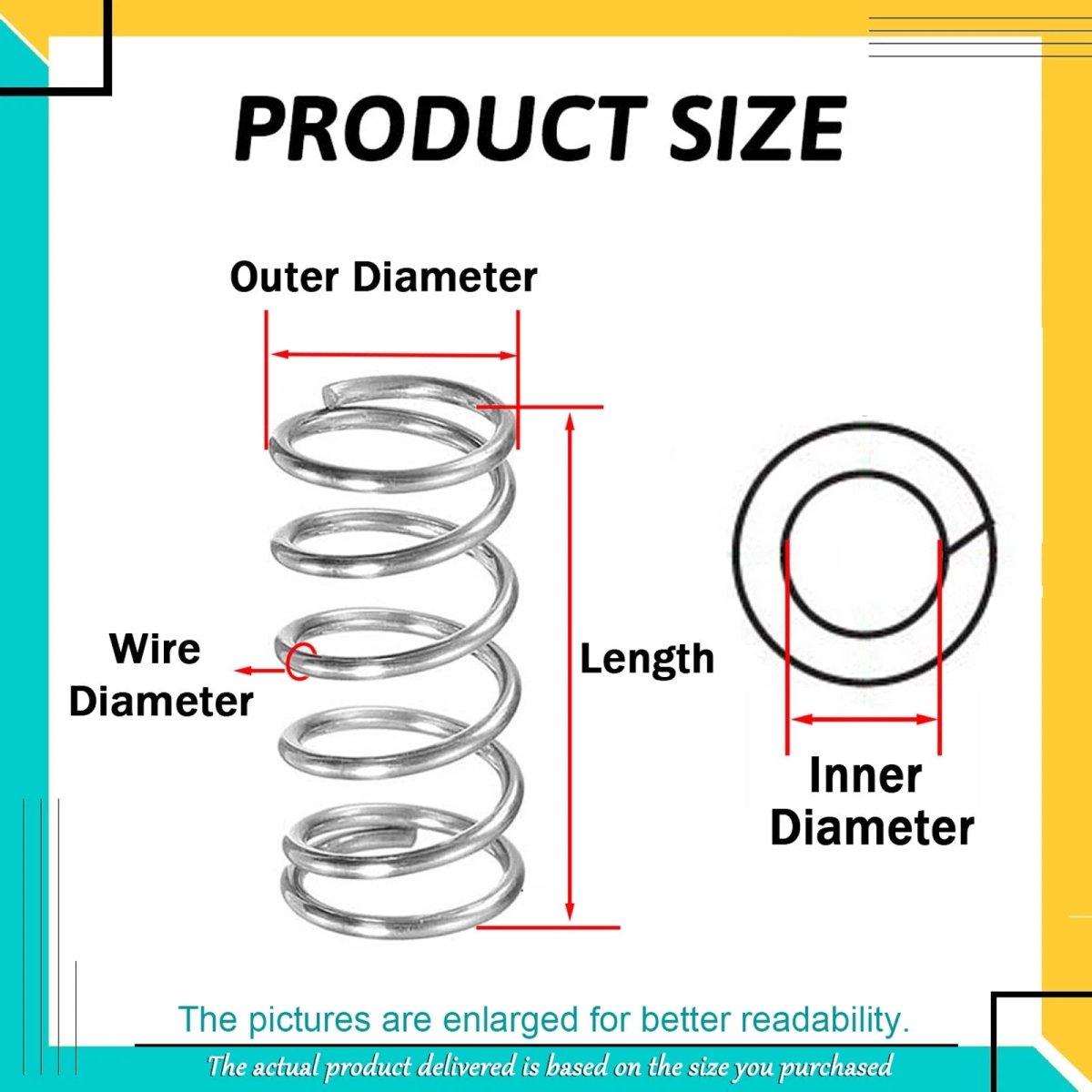
- Size: Match inner/outer diameters and free length to your project (use a “compression spring calculator” for precision).
- Load Capacity: Calculate maximum force using the “compression spring formula” (F = kx).
Pro Tip: For specialized needs like “valve spring compression tools” or “coil spring compressors,” check our step-by-step buying guides.
3. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Compress Springs Safely
Compressing springs requires caution. Follow these steps with a spring compression tool:
- Secure the Spring: Use a vise or clamp to prevent slippage.
- Attach the Tool: Align the compressor arms evenly (critical for “strut spring compression”).
- Apply Pressure Gradually: Avoid sudden force to prevent injury.
- Inspect After Compression: Check for deformities or stress marks.
Warning: Never attempt “how to compress coil springs without a tool” – improper methods risk damage or accidents.
4. Understanding Compression Spring Formulas
Physics governs spring behavior. Key equations include:
- Hooke’s Law: F = kx (force = spring constant × displacement).
- Energy Storage: The “energy in a compressed spring” is E = 0.5kx².
- Maximum Compression: Use “how to find maximum compression of a spring” guides to avoid overloading.
Example: Solving a “conservation of energy problem with spring compressed” involves calculating potential energy transfer.
5. Top Applications of Compression Springs
From cars to robotics, compression springs power countless systems:
- Automotive: Strut assemblies (“how to compress springs on struts”) and clutch mechanisms.
- Industrial: Valves, presses, and conveyor systems (“compression spring suppliers”).
- DIY Projects: Custom furniture, 3D printers, and toolkits (“small compression springs”).
Case Study: A customer used our “compression springs for sale” to rebuild a vintage motorcycle suspension – watch the video tutorial!
6. Where to Buy Quality Compression Springs
HomeDIYer stands out for:
- Custom Orders: Need a “30mm compression spring” or “conical compression springs”? We craft to spec.
- Competitive Pricing: Save vs. retailers like “compression springs Home Depot” or “Lowes.”
- Fast Shipping: Free delivery on orders over $50.
Compare: While “spring compression tool rental” is an option, owning tools ensures long-term savings.
FAQs
Q: How do I calculate spring rate?
A: Use our “compression spring calculator” or the formula k = Gd⁴/(8D³N), where G = material modulus.
Q: What’s the difference between compression vs extension springs?
A: Compression springs resist pushing forces, while extension springs handle pulling (learn more in “compression vs extension spring” guides).
Q: Can I reuse a compressed spring?
A: Yes, unless it’s deformed or part of a “heavy duty” application with cyclic loads.
Why Trust HomeDIYer?
With 15+ years in spring manufacturing, we combine expertise (“compression spring manufacturers”) with a passion for DIY innovation. Our blog covers everything from “how to compress suspension springs” to advanced “compression spring equations.”
Ready to Order? Browse our catalog of “compression springs near me” or contact us for custom quotes!